MCP: The Memory Layer for Decentralized AI
How the Model Context Protocol brings context-awareness, interoperability, and collective intelligence to autonomous agents across trustless systems.

We recently announced our intention to integrate an AI Toolkit and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) into our project, which will be a game-changer.
It’s time to understand the real impact this has on data systems. With more efficient communication, data can generate more assertive results.
We’re talking about the bridge between data and decisions: how the MCP is shaping the future of decentralized artificial intelligence.
What is the Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a communication protocol between artificial intelligence agents that share and update context in a structured and secure way.
It is designed for coordination between multiple models or autonomous agents that operate in decentralized systems, such as blockchains, decentralized AI platforms, or even multi-agent systems.
Simply, there are two very clear benefits. The first concerns communication/interoperability between agents, who now have access to the same information and the same code of conduct.
The second benefit lies in real-time data updates, a clear departure from the fixed nature of traditional static models.
Even if the agents are separated, it is as if everyone were in the same room, exchanging ideas and updating themselves all the time.
Why is MCP Necessary?
AI models (especially LLMs) are powerful, but they have limitations:
- They are static after training: Static AI models do not update themselves after training. It is like an encyclopedia from 2023, it has all the knowledge up until its publication, but does not include what was discovered afterwards.
- They have volatile memory, meaning they forget past contexts between interactions.
- In decentralized environments, multiple agents need to collaborate in real time, without relying on a central server.
MCP solves these problems by creating a standard for context switching between agents, ensuring:
- Persistence of relevant information.
- Efficient sharing of goals and data between agents.
- Coordinated execution of tasks across multiple layers.
How Does MCP Work?
It defines a standardized structure for the “model context”, the information and data that an AI model has access to when making decisions or generating responses.
In plain English, it means the background, details, or situational information the model uses to understand and respond to a task or question, including:
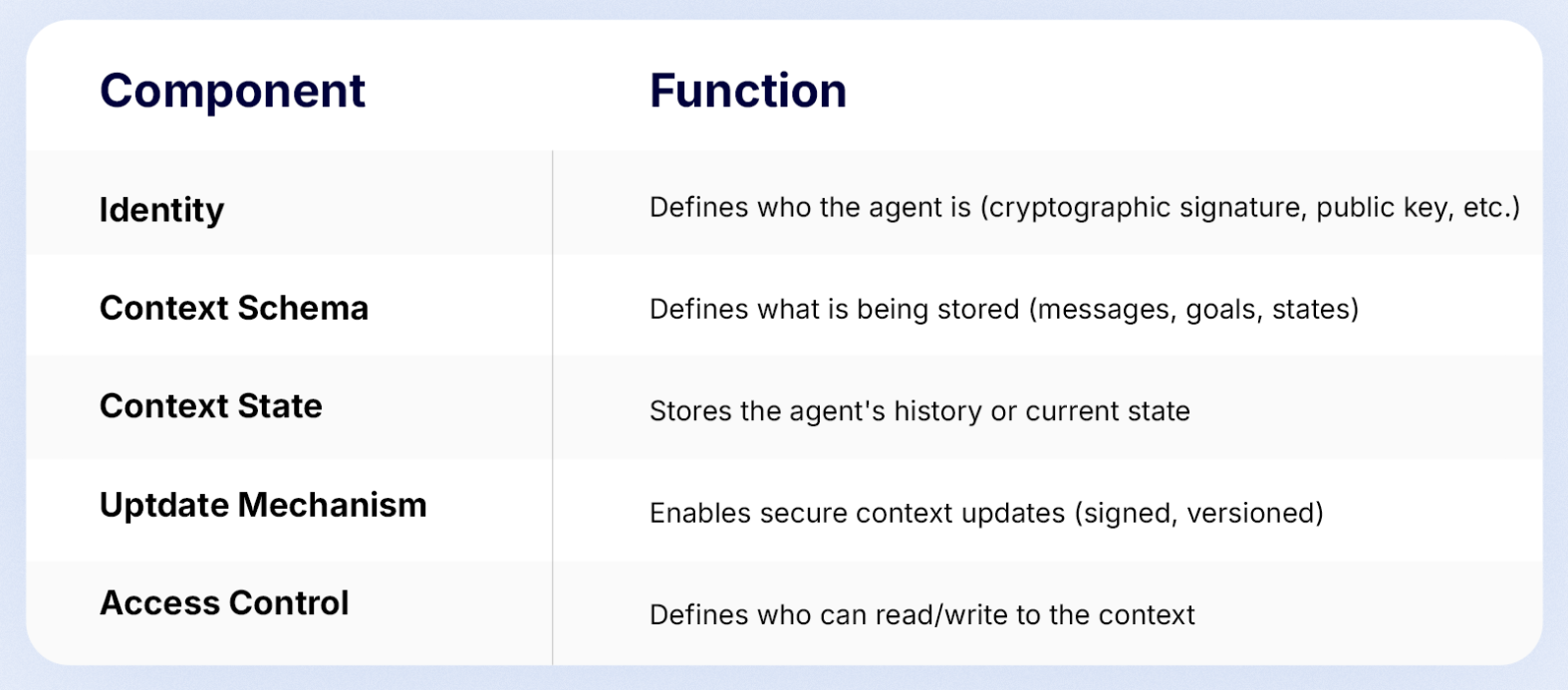
This context can be stored on-chain, off-chain, or via IPFS/Arweave, depending on the system architecture.
MCP Applications
An MCP application in decentralized AI is any AI agent or system that uses the Model Context Protocol to coordinate, access, and act upon data and tools across decentralized networks, enabling secure, scalable, and interoperable AI-powered workflows in blockchain and multi-agent environments.
Decentralized AI: Allows agents to share knowledge, history, and goals.
Real-Time Blockchain Analytics
An AI agent in a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform uses MCP to query live blockchain data (like transaction volumes, wallet activity, or token prices) from multiple decentralized sources.
The agent can then analyze this data to optimize trading strategies, manage liquidity pools, or trigger automated alerts, all without building a separate integration for each blockchain or data provider.Autonomous Smart Contract Auditing
A decentralized AI agent uses MCP to access and analyze smart contract code and transaction histories across various blockchains.
It can automatically audit contracts for vulnerabilities, verify compliance, and even suggest or execute fixes, providing continuous, autonomous oversight for decentralized applications (dApps).Agent coordination in DAOs or DeFi: Multiple bots operating in DeFi can align strategies using a common context.
Multi-Agent Coordination in Decentralized Systems
In a decentralized AI platform, multiple autonomous agents—each specializing in different tasks (e.g., data analysis, transaction execution, compliance monitoring), use MCP to coordinate and share context.
For instance, one agent fetches data from a blockchain, another interprets it, and a third executes a transaction, all communicating via standardized MCP interfaces rather than custom APIsPersonalized experiences: Users can carry their “history” across different agents, maintaining preferences and learnings.
Redundancy reduction: By sharing context, agents do not need to relearn everything from scratch.
Security and Privacy
MCP can be integrated with TEEs (Trusted Execution Environments) or ZKPs (Zero-Knowledge Proofs) to ensure that:
- Context is true, even if private.
- The origin of updates can be verified.
- There is no leakage of sensitive data between agents.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) enables decentralized AI systems to securely access diverse data sources by standardizing interactions, enforcing granular security controls, and maintaining interoperability across distributed environments.
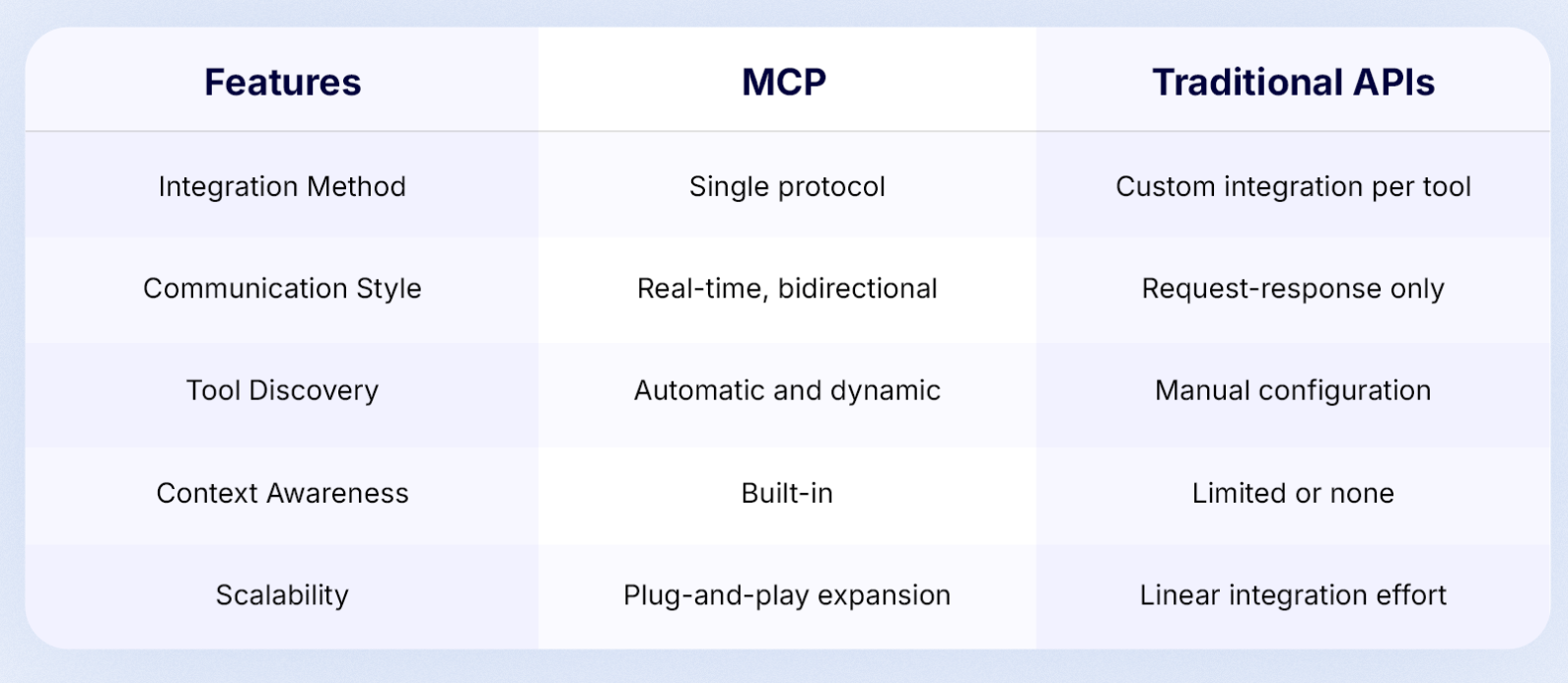
Core Mechanisms
1. Standardized, Permissioned Access
MCP acts as a universal connector between AI agents and decentralized data sources. Instead of building custom integrations for each system, developers use MCP’s open protocol to:
- Expose data sources via lightweight MCP servers (e.g., blockchain nodes, decentralized storage networks)
- Enforce access policies at the server level, such as restricting which files, smart contracts, or on-chain data an AI agent can retrieve.
2. Security-by-Design Architecture
MCP embeds security into its client-server model:
- Zero Trust Principles: Treats all components (hosts, clients, servers) as untrusted by default. Access requires explicit user consent and authentication (e.g., OAuth, API keys).
- Encrypted Communication: Data exchanges use HTTPS/TLS for remote connections, with optional MessagePack encoding for performance-critical applications.
- Granular Permissions: MCP servers can restrict actions (e.g., read-only access to specific database tables) and validate requests against predefined rules before execution.
Example 1: AI-Driven Inflation-Adjusted Stablecoin Management
A decentralized stablecoin protocol, like Nuon Finance, uses Truflation’s real-time inflation data to adjust interest rates or collateral ratios automatically. MCP facilitates secure coordination between multiple AI agents and decentralized data sources to achieve this.
Step-by-Step Workflow Using MCP:
Data Fetching (AI Agent 1 - Data Fetcher):
Uses MCP to query Truflation’s decentralized servers for the latest inflation rate (e.g., 3.2% as of May 2025). The MCP server validates the request, checks permissions, and returns encrypted data from Truflation’s 100M+ verified data points.
Risk Analysis (AI Agent 2 - Risk Model):
Processes the inflation data alongside on-chain metrics (e.g., collateralization ratios, liquidity pools) fetched via MCP from blockchains. The agent predicts whether the current stablecoin system is over- or under-collateralized relative to inflation trends.
Action Execution (AI Agent 3 - Smart Contract Updater):
If adjustments are needed, the agent uses MCP to propose updated parameters (e.g., raising interest rates by 0.5%) to Nuon’s smart contracts. The proposal is validated by MCP’s security rules (e.g., multi-signature approval) before execution.
Audit & Compliance (AI Agent 4 - Auditor):
Continuously monitors the system using MCP to pull Truflation data and cross-check contract logic. It flags discrepancies (e.g., stale inflation data) and triggers rebalancing via automated proposals.
Key MCP Features in Action
- Interoperability: MCP allows Nuon’s AI agents to interact with Truflation’s data servers, blockchain nodes, and smart contracts through a single protocol—no custom integrations needed.
- Security: Data requests are encrypted and permissioned, and Smart contract updates require MCP-mediated multi-party approval to prevent unilateral changes.
- Real-Time Coordination: MCP’s bidirectional communication lets agents share context and synchronize actions across decentralized systems.
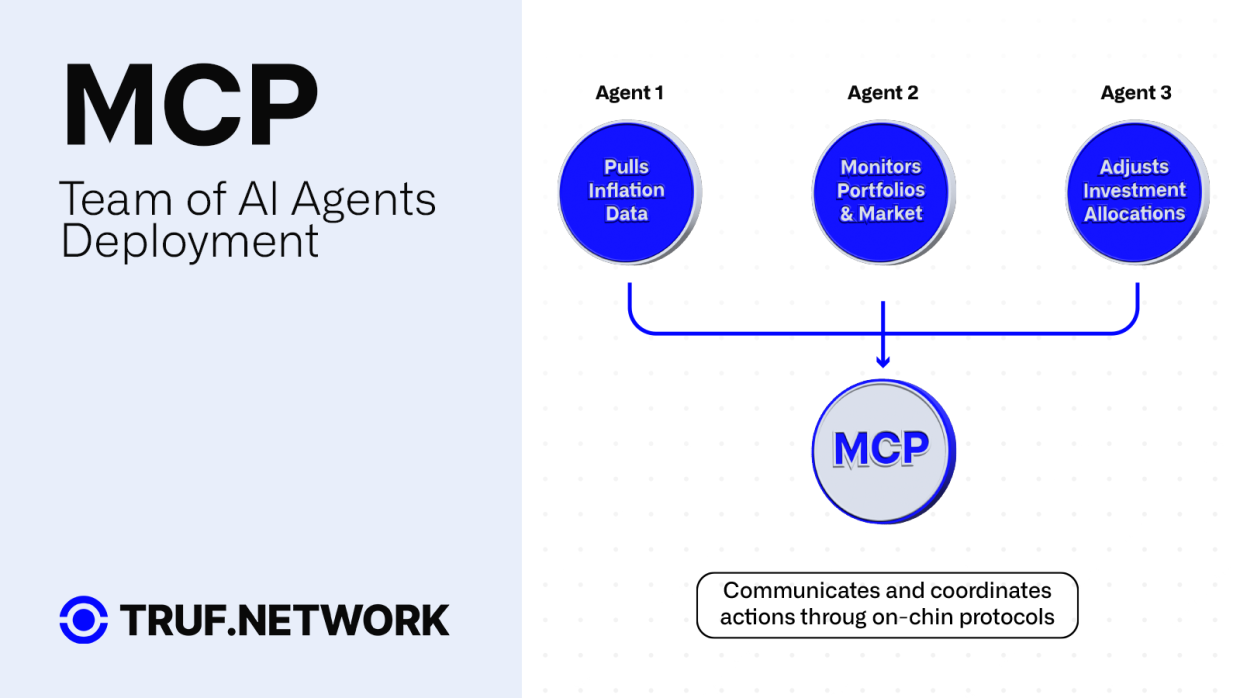
Example 2: Real-Time Inflation-Protected Investment Products
Suppose a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform wants to offer real-time inflation-protected investment products. Here’s how coordination would look.
The platform deploys a team of AI agents:
- One agent continuously pulls inflation data from Truflation.com.
- Another agent monitors user portfolios and market conditions.
- A third agent dynamically adjusts investment allocations to hedge against inflation.
All these agents communicate and coordinate actions through on-chain protocols, ensuring that the investment strategy adapts in real time as new data arrives.
The result: A transparent, automated, and decentralized financial product powered by the coordinated efforts of multiple AI agents and real-time data from Truflation.
This approach leverages Truflation’s decentralized data infrastructure as a foundation for multi-agent AI systems, enabling advanced financial products and analytics that are trustless, transparent, and resilient.
The Role of MCP in TRUF.NETWORK
In a decentralized data infrastructure like TRUF.NETWORK, where agents interact to collect, validate, and distribute real-time economic metrics, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) plays a foundational role.
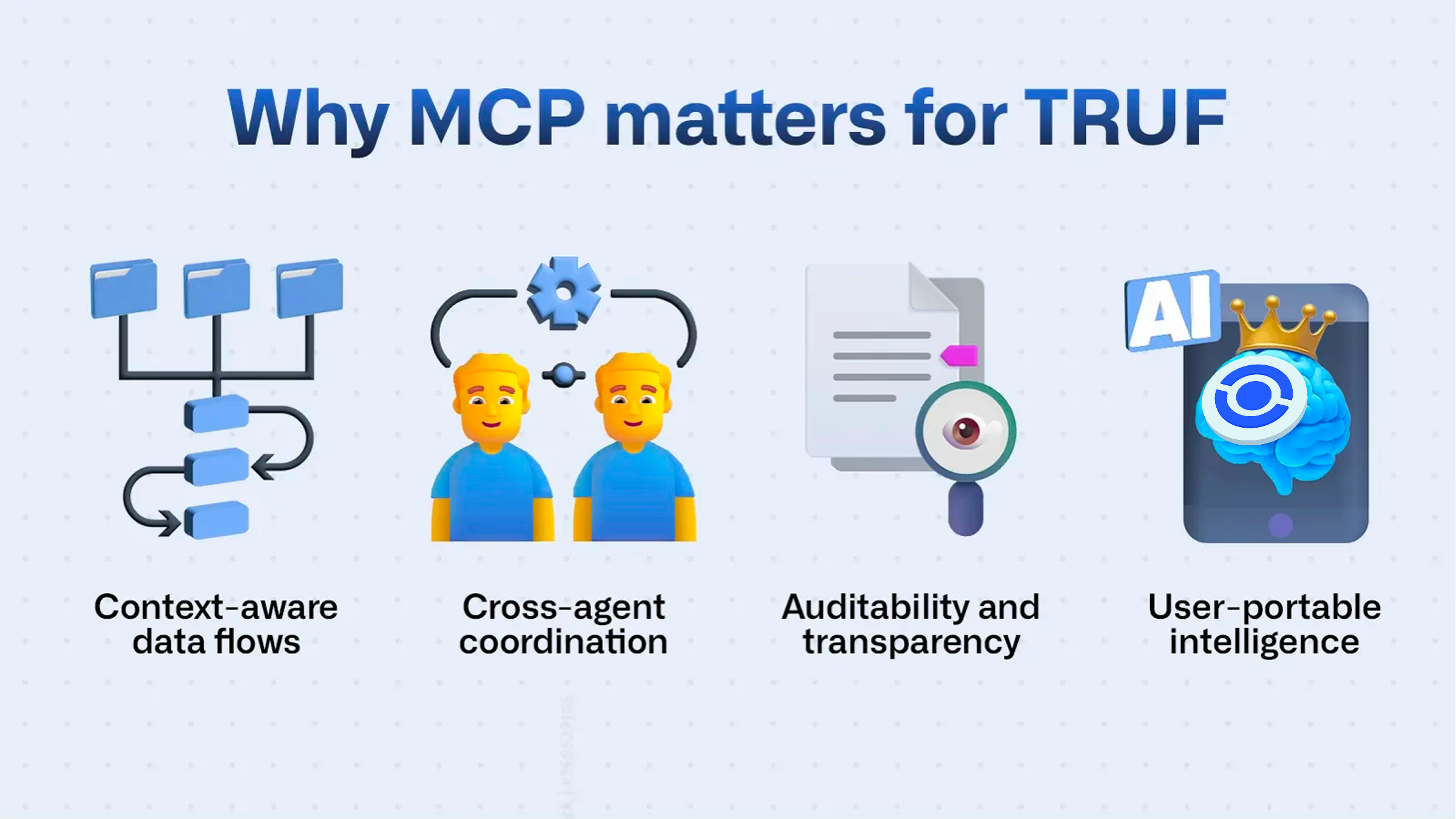
Why MCP matters for TRUF:
Context-aware data flows
TRUF agents don’t just transmit isolated data points. They collaborate in a system where past decisions, validation criteria, and source reliability need to be remembered and updated.
MCP allows these agents to share context in a structured, verifiable way, making the network smarter over time.Cross-agent coordination
From index construction to anomaly detection, multiple autonomous agents operate in parallel. MCP enables task alignment by allowing agents to declare and access shared goals, states, and updates, without centralized orchestration.Auditability and transparency
With MCP, each decision or update made by an agent can be traced to a specific context version, source, and cryptographic signature.
This enhances trust in the accuracy and neutrality of TRUF’s financial indices.User-portable intelligence
MCP supports personalized agent interactions, where user-defined parameters, previous queries, or trust preferences can travel between agents and apps, preserving continuity and user control.
In a network built around truthful data, MCP provides the memory and coordination logic that ensures the right agents are working with the right information, at the right time.
It turns passive data feeds into a collective intelligence system, where context isn’t lost, and decisions evolve together.
This is how TRUF.NETWORK doesn’t just distribute data. It builds understanding.
Final Thoughts
The Model Context Protocol is more than just infrastructure, the connective tissue allows decentralized AI agents to reason, adapt, and collaborate as a system.
By standardizing how context is stored, shared, and updated, MCP unlocks a new era of coordination: smarter workflows, reusable memory, and agents that learn from each other instead of operating in isolation.
- Interoperability: MCP provides a universal, open standard for connecting AI agents to a wide range of decentralized data sources and tools, eliminating the need for bespoke, one-off integrations.
- Security and Trust: MCP supports secure, auditable data access and action execution, which is crucial in decentralized and trustless environments like blockchains.
- Scalability: By standardizing how agents interact with data and each other, MCP enables decentralized AI systems to scale more easily and adapt to new data sources or tools as the ecosystem evolves
This is how AI becomes truly autonomous, not just in decision-making, but in understanding, remembering, and evolving together.

